(August 31, 2022) Java 2019: He had almost finished ploughing half of his paddy field. The plan was to finish the rest of the land before breaking for lunch. But just as he moved ahead, the machine got stuck and refused to budge despite several attempts. What he initially thought to be a big rock turned out to be a 140 cm high and 120 wide Lord Ganesha statue which took four days and 300 men to be excavated. Made of andesite, this 700-year-old headless and armless statue is one of the largest in the world.
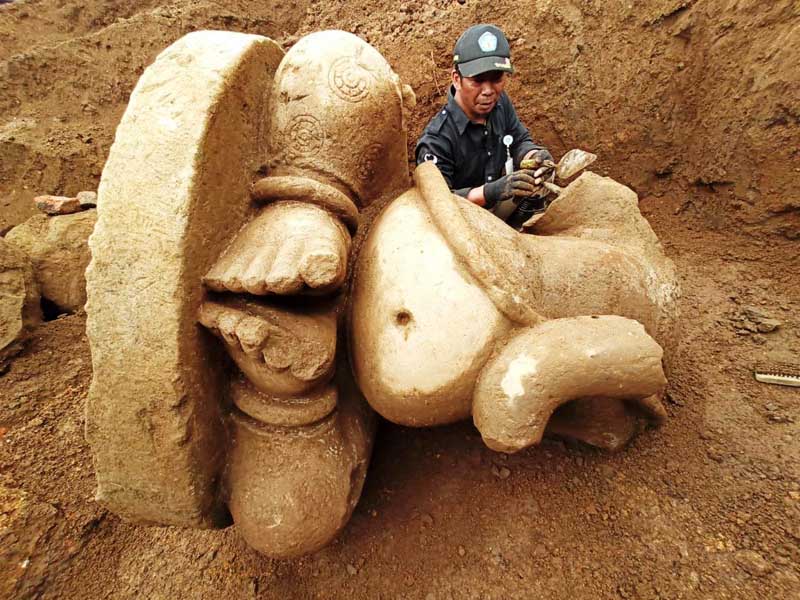

Ganesha statue unearthed in Java
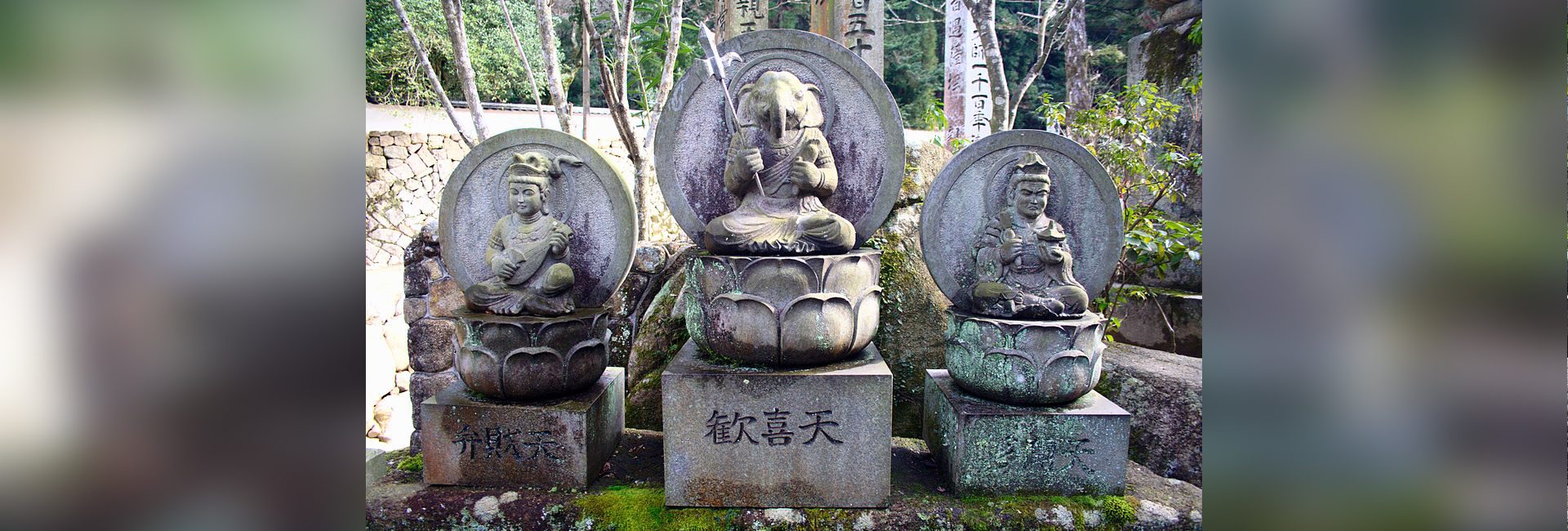
This is one of the many incidents where archaeologists have excavated full or parts of Lord Ganesha’s statues in various parts of the world. From far eastern Japan to Central America and South-East Asian island countries to Afghanistan – the trail of the elephant god can be traced back to about 2500 years. Interestingly, the god who is today revered before any auspicious event in Hindu households, first emerged only in the sixth century CE and was considered to be ‘Vighnakarta‘ or the creator of obstacles. However, over time, he evolved into ‘Vighnaharta’ or the remover of obstacles, who is revered to by the followers of many religions – including Buddhism, Jainism, Shinto and even Aztec.

Tibetan Ganpati
Global Indian sheds light on some uncovered trails of the god, who symbolises the universal concepts of knowledge, strength, and reverence.
From India to the far eastern shores
Way before the Europeans began their sea explorations, several empires in the Indian subcontinent had already established sea routes to various far eastern countries. Many merchants and scholars from these countries arrived on the Indian shores in search of wealth and knowledge. One such person, who came to the Kalinga Empire (present-day Odisha) in 8th Century CE, was a Japanese scholar named Kukai, who was keen to learn the secrets of Tantric Buddhism.
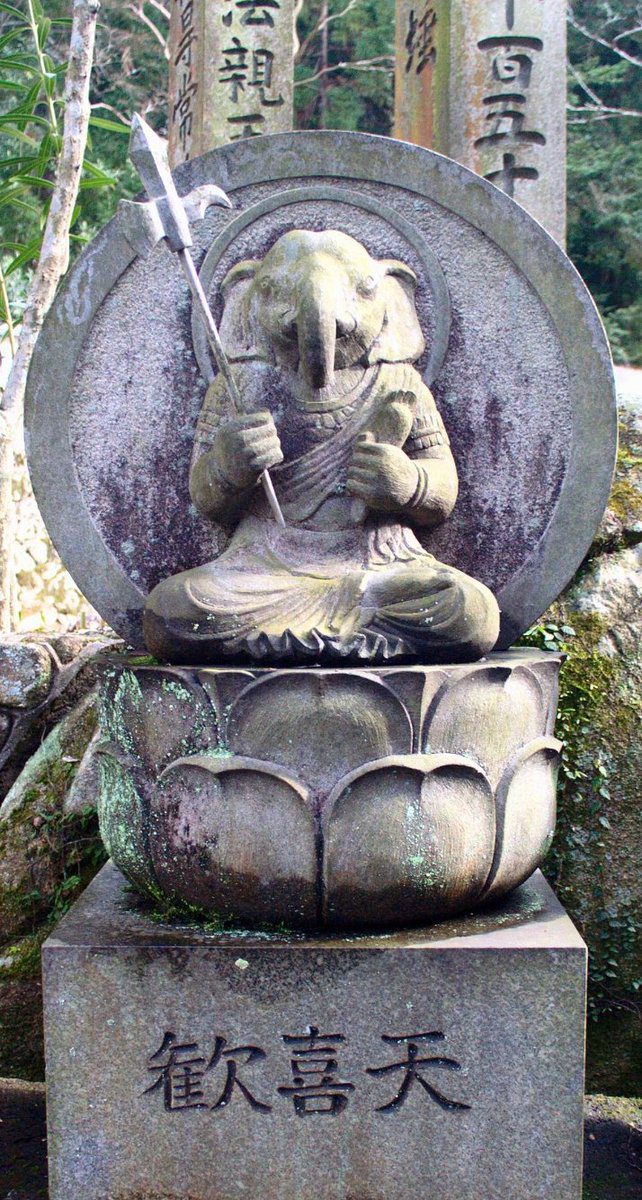

Japanese god, Kangiten
During his stay in Kalinga, Kukai met the noted Gandharan Buddhist scholar Pranja, who introduced him to various Hindu deities, some of whom later became a part of Shingon Buddhism in Japan. While most of these deities disappeared over time, only one survived over centuries and is still worshipped in over 250 temples across Japan. Named Kangiten, this god is depicted to have a head of an elephant and is otherwise famous among the locals as Lord Ganabachi or Binayaka Ten.

A 12th Century stone sculpture of Ganesha found in Cambodia
It is no secret that Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia is home to several temples that are dedicated to various forms of Lord Ganesha, but very few know that China is home to one of the oldest Ganesha statues in the world. Tucked away in the lush green forests of Kung-sin province, inside a Buddha temple is a rock-cut statue of Lord Ganesha, with the inscription 531 – referring to the year it was made in.
Land of the Méxica
When world-renowned European anthropologist Alexander Von Humbolt first postulated that the Aztec people worshipped a human deity, whose head resembled an elephant, many thought it to be a whimsy of a brilliant mind. The theory of Aztec symbols having any connection with an Indian deity then seemed unlikely to many as first, there were no sea routes connecting the two worlds, and second, elephants are not common in Central America.

The Aztec elephant god
However, later researchers found that Aztec depictions of the elephant had some religious significance. While it still remains unclear, the papers of prolific historian Donald Alexander Mackenzie (1873-1936) does throw some light on the connection between Central American and South Asian civilizations, and the possible exchange of cultures.
The Roman connection
In the 18th century British philologist, Sir William Jones drew close comparisons between the two-headed ancient Roman god Janus, and a particular form of Lord Ganesha, known as Dwimukhi-Ganesha. Calling Lord Ganesh the “Janus of India”, Sir Jones felt that there was a strong resemblance between the elephant god and the Roman god of beginnings.
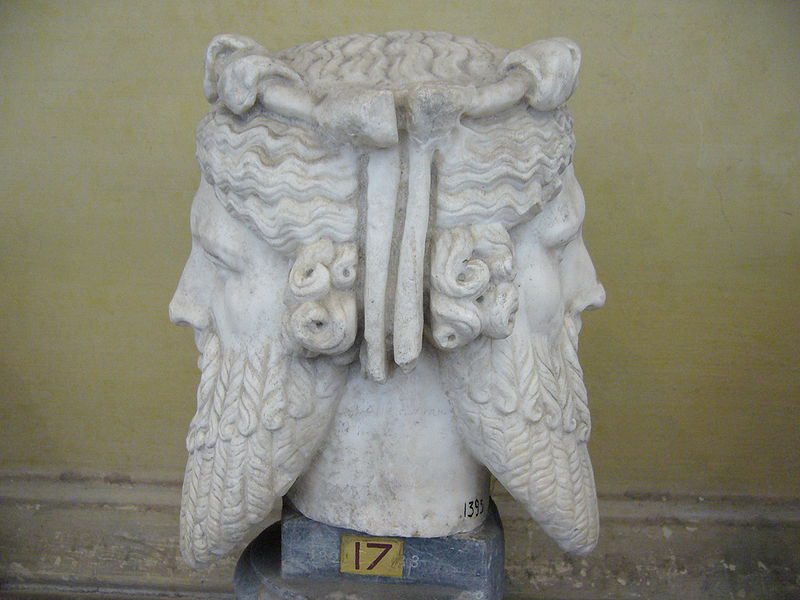

Two-Faced Janus at the Vatican Museum
Interestingly, the speculation was repeated by Volney in his 1791 publication, Meditation on the Revolutions of Empires, in which he pointed out the phonetic similarity between the names “Ganesha” and “Janus”. Later in his 1810 published book The Hindu Pantheon, Moor too expanded the claims of an association noting that Janus, just like Lord Ganesha, was invoked at the beginning of any undertakings.